ข้อมูลการปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุด (Best Practice) ของนครปูซาน สาธารณรัฐเกาหลี
นครปูซาน เมืองแห่งนวัตกรรม
ความจำเป็นในการสร้างเมืองแห่งนวัตกรรมของนครปูซาน
เมื่อวันที่ 24 มิถุนายน 2548 รัฐบาลสาธารณรัฐเกาหลีได้ประกาศแผนการกระจายอำนาจตามที่สถาบันสาธารณะ 176 แห่ง ได้ย้ายที่อยู่นอกเขตเมืองหลวงและเมืองแดจอนไปยังเมืองใหญ่ในภูมิภาค 12 เมือง โครงการย้ายถิ่นฐานได้กระตุ้นให้นครปูซาน โดยมุ่งเน้นการพัฒนาเพื่ออนาคต โดยการสร้างเมืองเฉพาะในภูมิภาค
ซึ่งอุตสาหกรรมในท้องถิ่น นักวิชาการ สถาบันการวิจัย และองค์กรอิสระในท้องถิ่นทำงานร่วมกันเพื่อส่งเสริมการเติบโตภายในภูมิภาค ตัวอย่างที่ประสบความสำเร็จในการพัฒนาเมืองแห่งนวัตกรรม สามารถพบได้ในเมืองอุตสาหกรรมที่ทันสมัย เช่น สวนเทคโนโลยี Sophia Antipolis ในสาธารณรัฐฝรั่งเศส,โตโยต้า ในประเทศญี่ปุ่น และเมืองคิสตา (Kista) ในราชอาณาจักรสวีเดน ซึ่งที่กล่าวมาทั้งหมดนี้สามารถยกระดับความสามารถในการแข่งขันทั้งในระดับภูมิภาคและในระดับประเทศผ่านโครงการต่าง ๆ โดยนครปูซานเมืองนวัตกรรมประกอบด้วย 3 เขตนวัตกรรม และพื้นที่ที่อยู่อาศัยแบบหลากหลาย เมื่อหน่วยงานต่าง ๆ มีการเคลื่อนย้าย: 4 หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเดินเรือและการประมง จะถูกเคลื่อนย้ายไปที่เขตดงซัม (Dongsam) หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภาพยนตร์
3 หน่วยงานจะถูกย้ายไปยังเขตเซนทัม (Centum) และ 5 สถาบันการเงินและสถาบันสาธารณะอื่น ๆ ไปยังเขตมุนฮยอน (Munhyeon) โดยจะมีการสร้างพื้นที่ที่อยู่อาศัยแบบหลากหลายเป็นจำนวนมาก ในพื้นที่ที่ศูนย์ปฏิบัติการด้านโลจิสติกส์ของกองทัพสาธารณรัฐเกาหลีเคยตั้งอยู่
แนวทางการดำเนินการจัดตั้งเมืองแห่งนวัตกรรมนครปูซาน
- เป้าหมาย: เพื่อขับเคลื่อนการพัฒนาเฉพาะภูมิภาค โดยมีพื้นฐานตามภาคส่วนที่แตกต่างกัน 3 ประการ ได้แก่ (ภาคส่วนการเดินเรือ / ภาคส่วนการประมง,ภาคส่วนการเงิน และภาคส่วนภาพยนตร์)
- เลือกเขตนวัตกรรม (30 มีนาคม 2549 กระทรวงที่ดิน การขนส่งและกิจการเดินเรือ) ▷3 เขต + พื้นที่ที่อยู่อาศัยแบบหลากหลาย (a multi-dwelling residential area)
- เขตดงซัม (Dongsam District) (ภาคส่วนการเดินเรือ / ภาคส่วนการประมง): มีหน่วยงานที่รับผิดชอบ
4 หน่วยงาน ได้แก่→สถาบันวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีมหาสมุทรเกาหลี, สถาบันการเดินเรือแห่งสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, สถาบันประสานงานการประมงแห่งชาติ, บริการจัดการคุณภาพผลิตภัณฑ์ประมงแห่งชาติ
- เขตมุนฮยอน (Munhyeon District) (ภาคส่วนการเงินและภาคส่วนอื่น ๆ ): มีหน่วยงานที่รับผิดชอบ
5 หน่วยงาน ได้แก่→ บริษัท หลักทรัพย์จัดการกองทุนสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, คลังสินเชื่อเพื่อที่อยู่อาศัยสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, ศูนย์รับฝากหลักทรัพย์สาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, บริษัท รับประกันการเคหะแห่งสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, บริษัท Korean Southern Power จำกัด
- เขตเซนทัม (Centum District) (ภาคส่วนภาพยนตร์และสื่อ): มีหน่วยงานที่รับผิดชอบ 3 หน่วยงาน→
สภาภาพยนตร์สาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, คณะกรรมการจัดอันดับสื่อสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, คณะกรรมการจัดอันดับเกม
- เขตแดยอน (Daeyeon District) (เขตที่อยู่อาศัยแบบหลากหลาย)
ความก้าวหน้าในการพัฒนาแต่ละเขต
- เขตดงซัม (Dongsam district)

สถานะเบื้องต้น
- ที่ตั้ง: 1125 ดงซัม-ดง, ยองโด-กู
- ขนาดพื้นที่: 616,000 ตารางเมตร
- หน่วยงานที่มีการย้ายพื้นที่: 4 หน่วยงานที่มีความเกี่ยวข้องกับกิจการทางทะเลและการประมง ได้แก่ สถาบันวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีทางมหาสมุทรแห่งสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, สถาบันทางทะเลแห่งสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, สถาบันสมุทรศาสตร์แห่งชาติ, การบริการจัดการคุณภาพผลิตภัณฑ์ประมงแห่งชาติ
※สถานที่ที่มีอยู่, สถานที่ตามแผน (9): สถาบันเทคโนโลยีการเดินเรือและการประมงของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, สถาบันวิจัยและฝึกอบรมสิ่งแวดล้อมทางทะเล, สำนักงานใหญ่ประจำภูมิภาคทางใต้ของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลีใต้ Coastguard, โรงเรียนมัธยมทางทะเลนครปูซาน, ท่าเรือข้ามฟากระหว่างประเทศ, สถานีดับเพลิงท่าเรือนครปูซาน พิพิธภัณฑ์ทางทะเลแห่งชาติ มหาวิทยาลัยทางทะเล (วิทยาเขตที่สอง), การท่าเรือนครปูซาน
- ทิศทางในการพัฒนา
- สร้างเมืองแห่งเทคโนโลยี (Technopolis ) ทางทะเลที่มีชื่อเสียงระดับโลก โดยจัดตั้งกลุ่มหน่วยงานที่รับผิดชอบทางทะเลและหน่วยงานที่รับผิดชอบการประมง
- สร้างเขตที่สำคัญและสวนพักผ่อนทางทะเล
- เขตมุนฮยอน (Munhyeon District)

สถานะเบื้องต้น
- ที่ตั้ง: อยู่บริเวณ 1227-2, มุนฮยอน-ดง, นัม-กู
- ขนาดพื้นที่: 102,000 ตารางเมตร เขตการการค้า
- หน่วยงานที่มีการย้ายพื้นที่: 11 สถาบัน (ย้ายที่ตั้งหน่วยงานสาธารณะ 5 แห่ง และสถาบันทางการเงินที่เกี่ยวข้อง 6 แห่ง)
- หน่วยงานสาธารณะที่จะย้าย (5): บริษัท หลักทรัพย์จัดการของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, บริษัท สินเชื่อที่อยู่อาศัยของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, ศูนย์รับฝากหลักทรัพย์ของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, บริษัท รับประกันการเคหะของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, บริษัท เกาหลีเซาท์เทิร์น
พาวเวอร์ จำกัด
- สถาบันการเงิน (6): ธนาคารแห่งสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี สาขานครปูซาน, ศูนย์แลกเปลี่ยนสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี (KRX), ธนาคารนครปูซานสำนักงานใหญ่, นองฮยับสำนักงานใหญ่ปรพจำนครปูซาน (Nonghyup Busan Headquarter), กองทุนเทคโนโลยี KIBO, กองทุนรับประกันเครดิตสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี
ทิศทางในการพัฒนา
- ดึงดูดธุรกิจและส่งเสริมกิจกรรมทางการเงินผ่านการแนะนำของศูนย์ทางการเงิน
- ใช้พื้นที่อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพผ่านสถาปัตยกรรมในการสร้างจุกสังเกตที่สำคัญ
- เขตเซนทัม (Centum District)

สถานะเบื้องต้น
ที่ตั้ง: 1466-2, ยู-ดง ฮึนแด-กู
ขนาดพื้นที่: 61,000 ตารางเมตร *พื้นที่สำหรับบริษัทผลิตสื่อมีเดีย 12,000 ตารางเมตร
หน่วยงานที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงพื้นที่: สภาภาพยนตร์สาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, คณะกรรมการจัดอันดับสื่อสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี, คณะกรรมการบริหารและจัดอันดับเกม
※สถานที่ที่จะถูกสร้าง (3): ศูนย์โรงภาพยนตร์ปูซาน, สถานที่เบื้องหลังการถ่ายทำ, ศูนย์วัฒนธรรมและเนื้อหา
- พื้นที่ที่อยู่อาศัยแบบหลากหลาย (Multi-dwelling residential area)
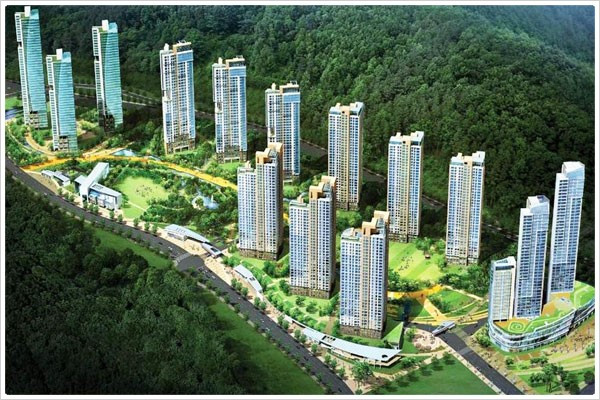

สถานะเบื้องต้น
ที่ตั้ง: 110-1, แดยอน-ดง, นัม-กู
ขนาดพื้นที่: 156,000 ตารางเมตร
สถานที่ที่จะถูกสร้างภายในพื้นที่ ได้แก่ อพาร์ตเมนต์ (2,304 ยูนิต), สตูดิโอ (112 แฟลต)
โรงเรียนประถม (1), โรงเรียนอนุบาล (2) ฯลฯ
การสร้างศูนย์กลางด้านอุตสาหกรรมและโลจิสติกส์ระหว่างประเทศ (Creation of the International Logistics and Industrial Complex)
โครงร่างของโครงการ
ชื่อโครงการ: การสร้างศูนย์กลางด้านอุตสาหกรรมและโลจิสติกส์ระหว่างประเทศ
ที่ตั้ง: บริเวณรอบ ๆ พื้นที่คังซอ (Gangseo), ปากแม่น้ำนักดงกัง (Nakdonggang)
พื้นที่: 33 ตารางกิโลเมตร
ระยะเวลาโครงการ: พ.ศ. 2551 (2008) ถึง พ.ศ. 2566 (2023)
※พัฒนาพื้นที่ 33 ตารางกิโลเมตร ในช่วงระยะแรก และหลังจากนั้นค่อยๆขยายพื้นที่การพัฒนา โดยขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการในการพัฒนา
ความจำเป็น
ความจำเป็นระดับชาติ
สนับสนุนการพัฒนาท่าเรือใหม่ของนครปูซาน (Busan New Port) ให้เป็นศูนย์กลางนานาชาติ ที่จะเป็นจริงตามชื่อ และเสริมสร้างความสามารถในการแข่งขันของประเทศ
ส่งเสริมการพัฒนาสนามบินนานาชาติกิมแฮและพื้นที่โดยรอบ
- เสริมสร้างการเชื่อมต่อระหว่างการท่าและกลุ่มอุตสาหกรรมโลจิสติกส์เพื่อนบ้าน
เปลี่ยนแปลงท่าเรือใหม่ของนครปูซาน (Busan New Port) ให้เป็นท่าเรือที่สร้างมูลค่า โดยการเพิ่มปริมาณสินค้าขาเข้า / ขาออกที่สูงขึ้น เพื่อเพิ่มความสามารถในการแข่งขันของประเทศในด้านการขนส่งสินค้า
ทางเรือ
- ส่งเสริมการเติบโตของประเทศโดยมีศูนย์กลางอยู่ที่ท่าเรือใหม่ของนครปูซาน (Busan New Port)
เพิ่มประโยชน์สูงสุดจากมูลค่าทางเศรษฐกิจบริเวณพื้นที่คังซอ (Gangseo) ซึ่งมีเงื่อนไขที่เหมาะสมกับ
การจัดตั้งท่าเรือ สนามบิน รถไฟ โดยมีถนนและแม่น้ำที่เชื่อมต่อกับเครือข่ายโลจิสติกส์ในประเทศและต่างประเทศ
ความจำเป็นระดับภูมิภาค
จัดตั้งกลุ่มอุตสาหกรรมโลจิสติกส์ขนาดใหญ่ที่มีการแข่งขันสูงในพื้นที่คังซอ (Gangseo) เพื่อลดต้นทุนด้าน
โลจิสติกส์ สร้างกลุ่มอุตสาหกรรม และเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพทรัพยากรมนุษย์
พัฒนาพื้นที่ให้เป็นจุดศูนย์กลางของการฟื้นฟูทางเศรษฐกิจสำหรับเขตเมืองใหญ่ทางตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
ซึ่งเป็นสายพานอุตสาหกรรมที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี โดยดึงดูดธุรกิจในประเทศและต่างประเทศที่โดดเด่น
ซึ่งในที่สุดจะนำไปสู่การพัฒนาประเทศที่สมดุล
แก้ไขปัญหาที่เผชิญการขาดแคลนที่ดินอย่างจริงจัง ของนครปูซานและพื้นที่ใกล้เคียง
ใช้ประโยชน์จากพื้นที่ เพื่อพัฒนาเป็นฐานการผลิตระดับโลกสำหรับชิ้นส่วนและวัสดุส่วนประกอบต่าง ๆ
ศูนย์โลจิสติกส์เอนกประสงค์ และศูนย์การลงทุนต่างประเทศ
ศักยภาพในการพัฒนาของพื้นที่คังซอ (Gangseo)
- ในประเทศ
- ท่าเรือใหม่ของนครปูซาน (Busan New Port) และสนามบินนานาชาติตั้งอยู่ในพื้นที่ ใกล้กับเขตการค้าเสรี (Free Economic Zones)
- สถานที่ตั้งศูนย์กลางในแถบอุตสาหกรรมตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ ที่ซึ่งมีการจัดกลุ่มโครงสร้างพื้นฐานที่สำคัญของประเทศ
- เป็นจุดเริ่มต้นและปลายทางในการพัฒนาทางน้ำและทางข้ามทวีปเพื่ออนาคตของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี
- ทำเลที่สำคัญสำหรับทั้งเส้นคยองบู (Gyeongbu Line) และเส้นยองฮอนัม (Yeonghonam Line) →
การพัฒนาพื้นที่คังซอ (Gangseo) นั้นคาดว่าจะทำให้เครือข่ายการจราจรในเขตเมืองมีความเป็นระเบียบและทันสมัยมากขึ้น
- เครือข่ายทิศใต้ – ทิศเหนือ ของถนนสายหลักที่สร้างขึ้นตามพื้นที่เกอเจ (Geoje), พื้นที่ของเมืองแตกู (Daegu) และพื้นที่ Saha ในพื้นที่ของนครปูซาน (Busan) ถนนที่ไปตามพื้นที่เมอร์ยาง (Miryang), พื้นที่
จิเฮย์ (Jihae) และสนามบินนานาชาติกิมแฮ นั้นจะถูกสร้างขึ้นในอนาคต
- ถนนตะวันตกและตะวันออก เชื่อมต่อกับพื้นที่จินแฮ (Jinhae) กับพื้นที่ซาฮา (Saha), พื้นที่ของนครปูซาน (Busan) และพื้นที่ซัมยางจิน (Samnyangjin) โดยถนนระหว่างพื้นที่ของนครปูซาน (Busan) และพื้นที่ชางวอน (Changwon) มีกำหนดการที่จะสร้างขึ้น
- ทางด่วนเชื่อมต่อพื้นที่ของนครปูซานและพื้นที่มาซานปูซานและแดกูรวมถึงถนนสองสายระหว่างมาซานและนครปูซานผ่านพื้นที่กิมแฮ (Gimhae) และพื้นที่ซัมยางจิน (Samnyangjin)

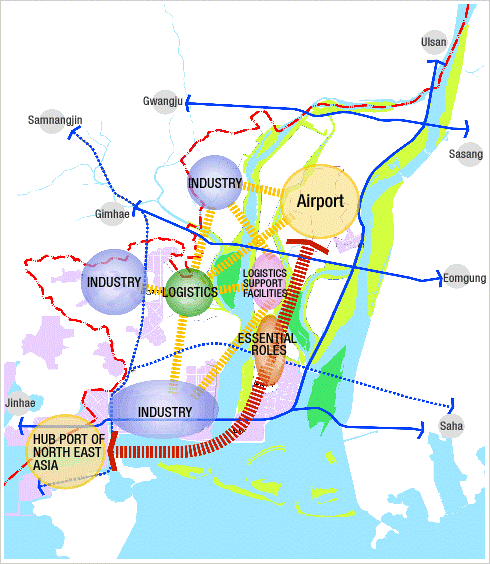
แผนภาพการพัฒนาพื้นที่คังซอ ของนครปูซาน สาธารณรัฐเกาหลี
ท่าเรือระหว่างประเทศและสนามบินนานาชาติตั้งอยู่ในพื้นที่→ศูนย์กลางของเครือข่ายโลจิสติกส์ระดับโลก
※บริเวณดังกล่าวจะเป็นจุดกระจายสินค้าที่สำคัญที่เชื่อมต่อเส้นทางกับทวีปอเมริกาและทวีปยุโรปเมื่อเส้นทางขั้วโลกเหนือเปิดในอนาคต โดยเส้นทางใหม่จะลดเวลาการเดินทางระหว่างท่าเรือนครปูซาน (Busan Port) และท่าเรือรอตเตอร์ดัม (Rotterdam Port) ลง 10 วัน ทำให้ลดค่าใช้จ่ายในการขนส่งลง 40% ผ่านอำนวยความสะดวกในการจัดตั้งเครือข่ายการกระจายสินค้ากับเมืองต่าง ๆ ในภาคตะวันออกของจีนและเมืองชายฝั่งตะวันออกไกลในสหพันธรัฐรัสเซีย และเชื่อมโยงกับภูมิภาคคิวชู ประเทศญี่ปุ่น
เพื่อสร้างเขตเศรษฐกิจของมหานครที่กว้างขึ้น
สามง่ามพัฒนาวิสัยทัศน์ระดับโลกของนครปูซาน
- พื้นที่ส่วนกลางของนครปูซาน (Central Busan Zone) เชื่อมต่อพื้นที่ยองบุ (Gyeongbu),
พื้นที่ยองกุย (Gyeongui) และบริเวณเขตแดนโชซอน ทองซินซา (Joseon Tongsinsa Lines)
- แกนของนครปูซานตะวันออกเชื่อมต่อสหพันธรัฐรัสเซียตะวันออก ชายฝั่งตะวันตกของประเทศญี่ปุ่นและชายฝั่งตะวันออกของคาบสมุทรสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี
- แกนของนครปูซานตะวันตก เป็นประตูสู่เอเชียตะวันออก โดยเชื่อมโยงทวีปเอเชีย ทวีปยุโรป และทวีปอเมริกาผ่านช่องแคบของสาธราณรัฐเกาหลี
ทิศทางการพัฒนา


โครงร่างการพัฒนาและองค์ประกอบของเมืองในอนาคต
ศูนย์อุตสาหกรรมเมืองหลวง ▷ 20 ตารางกิโลเมตร
- ตั้งอยู่ในทำเลที่เข้าถึงง่าย ใจกลางเขตอุตสาหกรรมของภูมิภาคตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ ศูนย์ดังกล่าวจะช่วยส่งเสริมเศรษฐกิจของประเทศอย่างมาก โดยการสร้างฐานอุตสาหกรรมระดับโลกสำหรับวัสดุชิ้นส่วนเครื่องจักรกล
- สถานะของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลีในฐานะพลังงานอุตสาหกรรมทางทะเลจะได้รับการรักษาความปลอดภัยผ่านการจัดตั้งศูนย์อุตสาหกรรมทางทะเลที่ให้บริการด้านการผลิต การกระจายการวิจัยและพัฒนา และการฝึกอบรม เป็นต้น
|
การจัดหมวดหมู่
|
หน้าที่หลัก
|
|
ศูนย์กลางความเชี่ยวชาญเฉพาะด้านอุตสาหกรรมในภูมิภาคตะวันออก
(Southeast Region specialized industry complex)
|
- สร้างฐานการผลิตระดับโลกสำหรับการเติบโตอุตสาหกรรมเฉพาะทาง เช่น เครื่องจักร,อุปกรณ์การต่อเรือ และอุตสาหกรรมชิ้นส่วนยานยนต์ (กลุ่มอุปกรณ์ขนส่ง)
- กลุ่มอุตสาหกรรมชิ้นส่วนหลัก (หนึ่งในเครื่องพัฒนาการเติบโตใหม่ของประเทศ) รวมถึงรถยนต์ที่เป็นมิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อม
('สีเขียว') เรือที่มีมูลค่าสูง, แบตเตอรี่พลังงานแสงอาทิตย์, เซลล์เชื้อเพลิง เป็นต้น
|
|
ศูนย์อุตสาหกรรมอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ที่เชื่อมต่อกัน (convergence devices industrial complex)
|
- กลุ่มอุตสาหกรรมอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ที่เชื่อมต่อกันอย่างทันสมัย โดยเกี่ยวข้องกับวัสดุขั้นสูง ชิ้นส่วนไอที และอุปกรณ์ที่ทันสมัย (เชื่อมโยงกับการขนส่งทางอากาศ)
- มีการใช้ประโยชน์จากทำเลที่ตั้งติดกับสนามบินนานาชาติกิมแฮ และกลุ่มการผลิต และการบำรุงรักษาสิ่งอำนวยความสะดวก รวมไปถึงชิ้นส่วนเครื่องบิน, เครื่องยนต์ เป็นต้น
|
|
ศูนย์อุตสาหกรรมทางน้ำ
(Marine industrial complex)
|
- พัฒนาการออกแบบโครงสร้างทางทะเลและอุตสาหกรรมการก่อสร้างที่ทันสมัยและอุตสาหกรรมการผลิตอุปกรณ์ทางทะเลและท่าเรือ
- พัฒนาอุปกรณ์สันทนาการทางทะเล (เรือยนต์ เรือยอชท์ เรือบรรทุกสินค้าส่วนตัว ฯลฯ ) อุตสาหกรรมการผลิตซึ่งเป็นอีกหนึ่งเครื่องมือขับเคลื่อนการเติบโตในอนาคตของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี
※ทำงานกับศูนย์อุปกรณ์สันทนาการทางทะเลและสถาบันเทคโนโลยีการต่อเรือขนาดกลางและขนาดเล็กในบริเวณใกล้เคียง
- เรียน วิจัย และสอนเทคโนโลยีทางทะเลใหม่ล่าสุด
|
|
ศูนย์การลงทุนต่างชาติ (Foreign investment complex)
|
- ดึงดูด บริษัทข้ามชาติและสถาบันวิจัยที่เกี่ยวข้องกับอุตสาหกรรมเฉพาะทางในภูมิภาคตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ให้เป็นฐานสำคัญของเครือข่ายการผลิตและการวิจัยระดับโลก
- สงวนที่ดินสำหรับ บริษัทการลงทุนต่างประเทศที่เชื่อมโยงกับเขตเศรษฐกิจเสรี
|
ศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ ▷ 9 ตารางกิโลเมตร
- จัดตั้งศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ระดับโลกที่เชื่อมโยงกับการขนส่งทางบกทางบกทางทะเลและทางอากาศ
- จุดยุทธศาสตร์ที่เลือกโดยรัฐบาลของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลีเพื่อเพิ่มผลกระทบของพื้นที่การค้าเสรี (FTA)
- สร้างประตูแห่งเอเชียเพื่อเตรียมพร้อมสำหรับขั้วโลกเหนือและเส้นทางรถไฟข้ามทวีป
|
การจัดหมวดหมู่
|
หน้าที่หลัก
|
|
การรวมกลุ่มและการดำเนินการของศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ (Complex logistics assembly and processing complex)
|
- สร้างศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ประกอบด้วย บริษัทด้านโลจิสติกส์ชั้นนำในประเทศ ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการจัดเก็บ การประกอบ การแปรรูป
การทำฉลาก และอื่น ๆ
- เป็นฐานโลจิสติกส์ที่สำคัญสำหรับการค้าและการดำเนินการค้านอกเขต โดยการจัดตั้งศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ร่วมกับบริษัทผู้ผลิตทั่วโลกที่เกี่ยวข้องกับฟังก์ชันการขนส่งของศูนย์โลจิสติกส์
|
|
ศูนย์วัสดุชิ้นส่วนระดับโลก
(Global parts materials supply complex)
|
- ทำหน้าที่เป็นฐานการผลิตระดับโลก สำหรับอุตสาหกรรมเฉพาะทางในภูมิภาคตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ เช่น อุปกรณ์ต่อเรือและชิ้นส่วนเครื่องจักรกลสำหรับใช้งาน และอุตสาหกรรมเรือสำราญและ
เรือยอชท์
- ทำหน้าที่เป็นฐานการผลิตระดับโลกสำหรับชิ้นส่วนยานยนต์ โดยดึงดูดศูนย์ประกอบชิ้นส่วนรถยนต์ (K / D (Knock Down)) จากพื้นที่ภายในประเทศและต่างประเทศ
|
|
ศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ทางทะเล ทางอากาศ
ทางราง และทางแม่น้ำ (SARR logistics complex)
|
- ลดต้นทุนโลจิสติกส์ด้านการขนส่งทางอากาศของเครื่องจักรและอุปกรณ์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ ในภูมิภาคตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ด้วยการสร้างศูนย์สินค้าพร้อมนำส่ง (RFC (Ready for Carriage)).
- รักษาหัวใจสำคัญด้านโลจิสติกส์ในเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงเหนือด้วยการจัดตั้งศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ทางทะเล ทางอากาศ ทางราง และทางแม่น้ำ (SARR) เพื่อเชื่อมโยงการขนส่งทางทะเล / อากาศ / รถไฟ / แม่น้ำ
|
|
อาคารและศูนย์สนับสนุน
(Complex terminal and support complex)
|
- สร้างอาคารศูนย์โลจิสติกส์ทางทะเล ทางอากาศ ทางราง และทางแม่น้ำ
|
ความรู้ – การสร้างเมือง ▷ 4 ตารางกิโลเมตร
- สร้างเมืองแห่งการสร้างองค์ความรู้ที่ยั่งยืนในอนาคต
- สร้างเมืองที่ดึงดูด ผู้คน ข้อมูล และทุน เพื่อเป็นแรงขับเคลื่อนการพัฒนานวัตกรรมสำหรับอุตสาหกรรมใหม่
- กลายเป็นเมืองสำคัญแห่งใหม่ในฐานะเมืองเวนิสแห่งใหม่ของเอเชียด้วยการสร้างคลองในเมืองที่เป็นมิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อม
|
การจัดหมวดหมู่
|
หน้าที่หลัก
|
|
เมืองแห่งการสร้างองค์ความรู้
|
- อุตสาหกรรมบริการความรู้: การเงินและการประกันภัย,การให้คำปรึกษาด้านการศึกษา การวิจัยและการพัฒนาการแพทย์ และอื่น ๆ
- ตลาดน้ำมันในเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงเหนือและการแลกเปลี่ยนการขนส่งระหว่างประเทศ
- ทัวร์ท่องเที่ยวทางทะเลชั้นยอดและเป็นเมืองพักผ่อนหย่อนใจ: การสันทนาการ ที่พักอาศัย ริมฝั่งทะเล
- ที่ตั้งของอาคารพักอาศัยชั้นยอด ตั้งอยู่ในสภาพแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติที่สวยงามและมีสภาพแวดล้อมที่น่ารื่นรมย์สำหรับชาวต่างชาติ
|
ผลที่คาดหวัง
- เพื่อเสนอทางออกพื้นฐานสำหรับปัญหาการขาดแคลนที่ดินเพื่ออุตสาหกรรมที่สำคัญของนครปูซาน
- เพื่อแปลงท่าเรือใหม่ของนครปูซานเป็นท่าเรือมูลค่าเพิ่มสูงที่ 'สามารถสร้างสินค้าขาเข้า / ขาออกในปริมาณมาก' โดยการพัฒนาควบคู่ไปกับกลุ่มอุตสาหกรรมโลจิสติกส์ใกล้เคียง และมีส่วนช่วยยกระดับความสามารถในการแข่งขันระดับชาติ
- ศูนย์กลางโลจิสติกส์ระดับโลก
- วางรากฐานเพื่อฟื้นฟูเศรษฐกิจของนครปูซานและพื้นที่เมืองเขตตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
- การสร้างงาน: 876,000 ตำแหน่ง ทั่วประเทศ 617,000 ตำแหน่ง ในภูมิภาคตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
- ผลเชิงบวกต่อการกระตุ้นการผลิต: 78 ล้านล้านวอนทั่วประเทศ, 53 ล้านล้านวอนในภูมิภาคตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
มาตราการบังคับใช้
- สร้างแนวคิดการพัฒนา (แผนแม่บท) เพื่อสร้างเมืองโลจิสติกส์ระหว่างประเทศ โดยแบ่งพื้นที่พัฒนาทั้งหมดออกเป็นหลายส่วนและทำการพัฒนาแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
- ดำเนินการพัฒนาพร้อมกับโครงการระดับชาติอื่น ๆ เพื่อเพิ่มขีดความสามารถในการแข่งขันของประเทศและภูมิภาค
- ฝั่งตะวันตกของแม่น้ำนักดงกัง (Nakdonggang River) ฝั่งตะวันตก (ด่านแรก): ได้รับการพัฒนาอย่างอิสระโดยรัฐบาลของนครปูซาน (9.65 ตารางกิโลเมตร)
- ฝั่งตะวันออกของแม่น้ำตะวันตกนักดงกัง (ระยะที่สอง): ได้รับการกำหนดและพัฒนาให้เป็นศูนย์อุตสาหกรรมแห่งชาติ (23.35 ตารางกิโลเมตร
- ดำเนินการกับการพัฒนาแบบบูรณาการกับเมืองนานาชาติมยองกี ( Myeonggi International City) ของบริษัทบ้านและที่ดินของสาธารณรัฐเกาหลี (Korea Land and Housing Corporation)
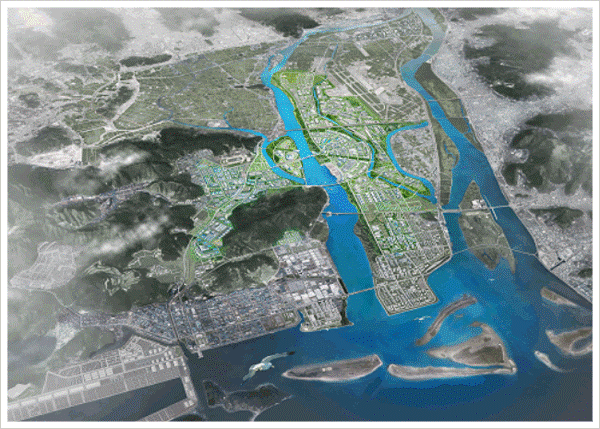
แนวความคิดการพัฒนา
มุมมองจากที่สูง (Bird’s Eyes View)
Necessities for Creating Busan Innovation City
In June 24, 2005, the Korean government announced a decentralization plan according to which 176 public institutions were relocated outside the capital region and Daejeon to 12 regional metropolitan cities. The relocation project prompted Busan city to construct a future-oriented, region-specific city where local industries, academia, research institutions and local autonomous organizations work together to foster regional growth. Examples of successful outcomes of the Innovative City project can be found in cutting-edge industrial cities such as Sophia Antipolis in France, Toyota, Japan and Kista, Sweden, all of which managed to enhance their regional and national competitiveness through the project. Busan Innovative City consists of three innovation districts and a multi-dwelling residential area once other agencies are relocated: four agencies related to maritime and fisheries will be relocated to the Dongsam district, three film-related agencies to the Centum district, and five financial and other public institutions to the Munhyeon district. A multi-dwelling residential area will be built on a lot where ROKA(Republic Korea Army) Logistics Command used to be located.
Busan Innovation City Construction Outline
- Goal : Drive region-specific development based on three different functions (maritime/fisheries, finance, film)
- Select Innovation districts (March 30, 2006, Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs)
- ▷ three districts + a multi-dwelling residential area
- Dongsam District (Maritime/Fisheries functions): four agencies → Korea Institute of Ocean Science & Technology, Korean Maritime Institute, National Oceanographic Institute, National Fishery Products Quality Management Service
- Munhyeon District (Finance and other functions): five agencies → Korean Management Asset Corporation, Korean Housing Finance Corporation, Korean Securities Depository, Korean Housing Guarantee Corporation, Korean Southern Power Co., Ltd.
- Centum District (Film and Media functions): three agencies → Korean Film Council, Korean Media Rating Board, Game Rating Board
- Daeyeon District (Multi-dwelling residential area)
Progress by district
- Dongsam district

Basic status
- Location: 1125 Dongsam-dong, Yeongdo-gu
- Space: 616,000㎡
- Agencies to be relocated: four agencies related to maritime affairs and fisheries → Korea Institute of Ocean Science & Technology, Korean Maritime Institute, National Oceanographic Institute, National Fishery Products Quality Management Service
※ Existing facilities, Planned facilities (9): Korean Institute of Maritime and Fisheries Technology, Marine Environment Research & Training Institute, South Regional Headquarters Korea Coastguard, Busan Maritime High School, International Ferry Terminal, Busan Harbor Fire Station, National Maritime Museum, Korea Maritime University (Second Campus), Busan Port Authority
Development direction
- Create a world-famous marine technopolis by forming a cluster of maritime and fisheries agencies
- Create district landmarks and a marine leisure park
- Munhyeon district

Basic status
- Location: area around 1227-2, Munhyeon-dong, Nam-gu
- Size: 102,000㎡, commercial district
- Institutions to be relocated: 11 institutions (five relocating public agencies, six relevant financial institutions)
- Public agencies to be relocated (5): Korean Manage Asset Corporation, Korean Housing Finance Corporation, Korean Securities Depository, Korean Housing Guarantee Corporation, Korean Southern Power Co., Ltd.
- Financial institutions (6): The bank of Korea Busan branch, Korean Exchange(KRX), Busan Bank head office, Nonghyup Busan headquarters, KIBO technology fund, Korea Credit Guarantee Fund
Development direction
- Attract businesses and promote financial activities through introduction of a financial complex
- Use space effectively through Landmark architecture
- Centum district

Basic status
- Location: 1466-2, U-dong, Haeundae-gu
- Space: 61,000㎡ filmㆍmedia related organizations 12,000㎡
- Agencies to be relocated: Korean Film Council, Korean Media Rating Board, Game Rating and Administration Committee
※ Facilities to be built (3): Busan Cinema Center, Post-Production Facility, Culture and Contents Complex
- Multi-dwelling residential area

Basic status
- Location: 110-1, Daeyeon-dong, Nam-gu
- Space 156,000㎡
- Facilities to be built within the area: apartments (2,304 units), studio (112 flats) elementary school (1), kindergarten (2), etc.
Creation of the International Logistics and Industrial Complex
Project Outline
- Name of the project: Building an international industrial logistics complex
- Location: Around the Gangseo area, Nakdonggang River Estuary
- Space: 33 ㎢
- Project period: 2008 to 2023
※ Develop an area of 33 ㎢ during the first stage, and then extend the development area gradually, depending on development needs.
Necessity
National necessity
- Encourage the development of Busan New Port to make it an international hub port that will be true to its name, and contribute to strengthening national competitiveness
Promote the development of Gimhae International Airport and its surrounding area.
- Reinforce connections between the port and the neighboring industrial logistics cluster
Transform Busan New Port into a high value-added port generating higher volumes of inbound/outbound cargo, to heighten national competitiveness in the field of harbor logistics.
- Further national growth centering around Busan New Port
Make the most of the economic value of the Gangseo area, which has optimal conditions with its port, airport, railway, roads and rivers connected in domestic and overseas logistics networks.
Regional necessity
- Establish a highly competitive large-scale industrial logistics complex in the Gangseo area, capable of reducing logistical costs, forming an industrial cluster and optimizing human resources.
Develop the area into a focal point of economic revival for the Southeast metropolitan area, the largest industrial belt in Korea, by attracting outstanding domestic and overseas businesses that will, subsequently, contribute to balanced national development.
- Solve serious land shortage problems facing Busan City and the nearby areas.
Make full use of the area as a global supply base for parts and component materials, a multi-logistics complex and a foreign investment complex.
Development potential of the Gangseo area
Domestic
- Busan New Port and an international airport to be located in the area. Proximity to the Free Economic Zones.
- Central location in the southeast industrial belt where key national infrastructure is clustered.
- Starting point and terminus of a future pan-Korea waterway and transcontinental railroad.
- Ideal location on both the Gyeongbu Line and Yeonghonam Line → the development of the Gangseo area is expected to make the metropolitan traffic network more organized and advanced.
- South-North network of major trunk roads built along Geoje, Daegu and Saha in Busan.
Roads along Miryang, Jihae and Gimhae International Airport are scheduled to be built in the future.
- West-East roads connecting Jinhae and Saha, Busan and Samnyangjin, and later, a road between Busan and Changwon are all scheduled to be built.
- An expressway connecting Busan and Masan, Busan and Daegu, as well as two roads between Masan and Busan through Gimhae and Samnyangjin.

International
- An international port and an international airport are located in the area→ the center of a global logistics network.
※ It will be a major goods distribution spot connecting American and European routes when the North Pole Route opens in the future. (The new route will cut down the travel time between Busan Port and Rotterdam Port by 10 days leading to a 40% reduction in costs.)
- Facilitate the formation of goods distribution networks with cities in the eastern part of China, and Far East coastal cities in Russia.
- Link with Kyushu, Japan to establish a wider metropolitan economic zone.
Three Development Prongs of Busan’s Global Vision
- Central Busan Zone connecting the Gyeongbu, Gyeongui, and Joseon Tongsinsa Lines
- The axis of East Busan connecting East Russia, the West coast of Japan and the Korean Peninsula’s East coast
- The axis of West Busan, the Gateway of East Asia, connecting Asia, Europe and the Americas through the Straits of Korea
Development Directions

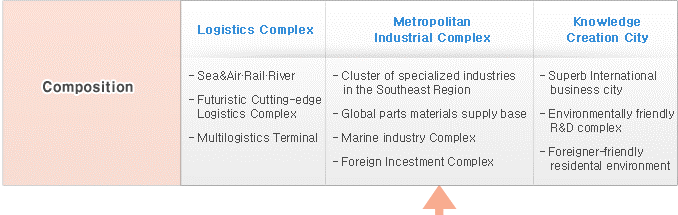

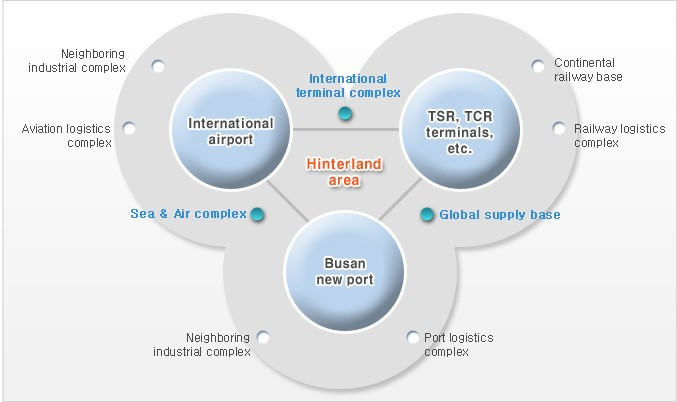
Development outline and composition of the future city
Metropolitan industrial complex ▷ 20㎢
- Conveniently located at the heart of the Southeast Region's industrial belt, the complex will greatly contribute to boosting the national economy by establishing a world-class industrial base for mechanical parts materials.
- Korea's status as a marine industry power will also be secured through the establishment of the marine industrial complex, offering multiple production, distribution, R&D and training functions, etc.
|
Classification
|
Main Functions
|
|
Southeast Region specialized industry complex
|
- Create a global supply base for fast-growing local specialized industries such as machine, shipbuilding equipment and automobile parts industries. (Transportation equipment cluster)
- Cluster core parts materials industries (one of the new national growth engines) including environmentally friendly ('green') automobiles, high value-added vessels, solar batteries, fuel cells, etc.
|
|
convergence devices industrial complex
|
- Cluster cutting-edge convergence devices industries that involve advanced materials, IT parts and state-of-the-art equipment (linked with aviation transport).
- Take advantage of its location adjacent to Gimhae International Airport, and cluster production and maintenance facilities including aircraft parts, engines, etc.
|
|
Marine industrial complex
|
- Develop cutting-edge marine structural design and building industries and the marine and harbor equipment manufacturing industry
- Develop the marine leisure equipment (motorboats, yachts, personal watercraft, etc.), manufacturing industry, which is another future growth engine in Korea.
※ Work with marine leisure equipment centers, and small and medium shipbuilding technology institutes nearby.
- Study research and teach the latest marine technology.
|
|
Foreign investment complex
|
- Attract multi-national corporations and research institutes involved with specialized industries to the southeast region as a Key base of global production and research networks.
- Reserve land areas for foreign investment companies, linked with free economic zones.
|
Logistics Complex ▷ 9㎢
- Establish a global logistics complex linked with international land, sea and air transport facilities.
- A strategic point chosen by the Korean government to maximize the effects of FTAs.
- Build a Eurasian Gateway in preparation for North Pole and transcontinental railway routes.
|
Classification
|
Major Functions
|
|
Complex logistics assembly and processing complex
|
- Establish a logistics complex comprised of top domestic logistics companies dealing with storage, assembly, processing, labeling, etc.
- Become a key logistics base for Outward Processing Trade by establishing a logistics complex with global manufacturing companies involving complex logistics functions.
|
|
Global parts materials supply complex
|
- Serve as a global supply base for specialized industries in the Southeast Region such as shipbuilding equipment and implements, mechanical parts and the cruise & yacht industry.
- Serve as a global supply base for automobile parts by attracting automobile centers (K/D(Knock Down)) from other domestic areas and abroad.
|
|
SARR logistics complex
|
- Reduce logistics costs of machine and electronics air freight in the Southeast Region by building an RFC (Ready for Carriage) center.
- Secure a pivotal position in logistics in Northeast Asia by establishing a SARR logistics complex linking sea/air/rail/river transport nodes.
|
|
Complex terminal and support complex
|
- Build a SARR (Sea-Air-Rail-River) terminal complex.
|
Knowledge - Creating City ▷ 4㎢
- Build a sustainable future-oriented knowledge creation city.
- Build a core city that attracts people, information and capital to become a driving force for innovative new industries.
- Become a new landmark city as the new Venice of Asia by creating an environmentally friendly canal city.
|
Classification
|
Major Functions
|
|
Knowledge Creation City
|
- Knowledge services industry: finances and insurance, consulting, education, medical R&D, conventions, etc.
- Northeast Asian oil market and international shipping exchange.
- High-class marine tour leisure city: recreation, leisure, accommodation, waterfront.
- Location of a top-class residential complex nestled in a beautiful natural environment and offering a pleasant living environment for foreigners.
|
- To offer a fundamental solution for Busan city's chronic shortage of prime industrial plots.
- To transform Busan New Port into a high value-added port that 'generates a high amount of inbound/outbound cargo' by developing it alongside the neighboring industrial logistics cluster, and to ultimately make a huge contribution to national competitiveness.
- Global logistics hub
- Laying a foundation to revitalize the economy of Busan and also the Southeast metropolitan area.
- Job creation: 876,000 jobs nationwide, 617,000 jobs in the southeast region.
- Positive effect on production inducement: 78 trillion won nationwide, 53 trillion in the Southeast region.
- Enforcement method
- Establish development concept (master plan) to build an international logistics city, divide the entire development area into several sections and make gradual phased development.
- Carry out development along with other national projects to raise national and regional competitiveness.
- West bank of the West Nakdonggang River (first stage): to be developed independently by Busan Metropolitan City (65 ㎢).
- East bank of West Nakdonggang River (second stage): to be designated and developed as a National Industrial Complex (35 ㎢).
- Proceeding with integrated development with Myeonggi International City (Korea Land and Housing Corporation).
- Development Concept


Retrieved From: 1. https://english.busan.go.kr/bsinnocity
- https://english.busan.go.kr/bslogicpro01
- https://english.busan.go.kr/bslogicpro02
- https://english.busan.go.kr/bslogicpro03
เอกสารแนบ : Best Practice - นครปูซาน Innovation City and Logistics Hub (อภิชัย).pdf