ข้อมูลการปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุด (Best Practice) ของจังหวัดฟูกูโอกะ ประเทศญี่ปุ่น
การเติบโตสีเขียวของเมืองคิตะคิวชู
บทนำ
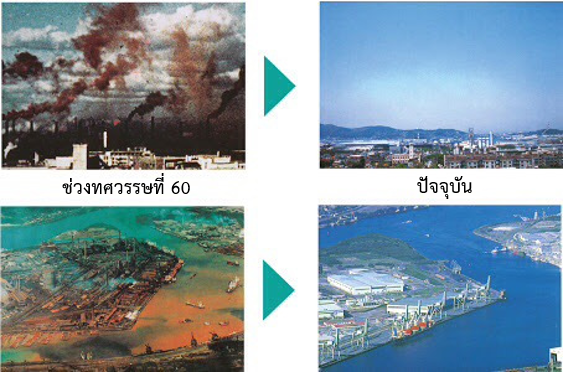
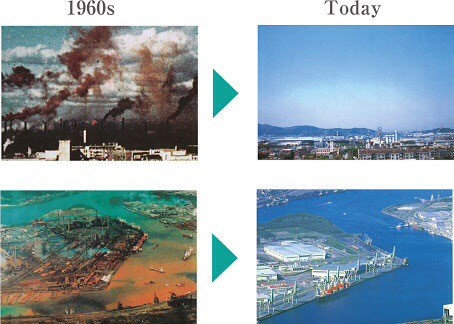
เมืองคิตะคิวชูตั้งอยู่ในจังหวัดฟูกูโอกะซึ่งอยู่ทางฝั่งตะวันตกของหมู่เกาะคิวชู เมื่อ พ.ศ. 2444 ได้รับการพัฒนาให้เป็นเมืองแห่งอุตสาหกรรมการผลิตส่งผลให้เกิดมลพิษทางอากาศและทางน้ำในช่วงทศวรรษที่ 60 ในเวลาต่อมา ผู้ที่เกี่ยวข้องโดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งประชาชนได้ร่วมกันทำงานอย่างหนักเพื่อปรับปรุงสภาพสิ่งแวดล้อมให้ท้องฟ้าและมหาสมุทรในคิตะคิวชูกลับมามีสีครามสดใสได้อีกครั้ง ประสบการณ์เหล่านี้ทำให้เมืองคิตะคิวชูได้มีโอกาสพัฒนาอุตสาหกรรมใหม่ ๆ รวมถึงเทคโนโลยีด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมอย่างต่อเนื่องจนกลายเป็นเมืองอัจฉริยะ
ที่เป็นมิตรต่อสิ่งแวดล้อม อีกทั้ง มีการหมุนเวียนของทรัพยากรและเป็นแหล่งพลังงานหมุนเวียน
แผนปฏิบัติการ
- การพัฒนาอุตสาหกรรมและการเอาชนะมลพิษ
- ความร่วมมือและธุรกิจระหว่างประเทศด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
- บทบาทของคิตะคิวชูในการส่งเสริมเป้าหมายการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน
เมืองแห่งผู้นำด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมที่ทันสมัย
2539 แผนปฏิบัติการ 21 เพื่อการพัฒนายั่งยืน (Agenda 21)
2541 โครงการเมืองนิเวศ (Eco-Town)
2543, 2549 ระบบค่าธรรมเนียมกำจัดขยะ
2547 โครงการสุดยอดการออกแบบเมืองหลวงแห่งการพัฒนาที่ยั่งยืนของโลก (The Grand Design for a World Capital of Sustainable Development)
2552 เมืองต้นแบบด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม (ECO-Model City) (ภายใต้การดูแลของรัฐบาลกลาง)
2555 โครงการริเริ่มเมืองอนาคตและเมืองจำลองเขตยุทธศาสตร์ระหว่างประเทศ (Future City Initiative & Int’l Strategic Zone Model City) (ภายใต้การดูแลของรัฐบาลกลาง)
2560 แผนงานด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมขั้นพื้นฐานที่สอดคล้องกับเป้าหมายการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน
เทคโนโลยีด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม

การประเมินผลระดับนานาชาติ
2528 รายงานการกำกับดูแลกิจการในเอเชีย หรือที่เรียกว่า “White Paper” โดยองค์การความร่วมมือทางเศรษฐกิจและการพัฒนา (OECD) เรื่องการเปลี่ยนเมืองจากสีเทาเป็นสีเขียว
2533 โครงการสิ่งแวดล้อมแห่งสหประชาชาติ (UNEP) มอบรางวัล Global 500 Award
2535 Local Government Honours ณ การประชุมริโอ
2543 การจัดการประชุมรัฐมนตรีคณะกรรมาธิการเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งสหประชาชาติสำหรับเอเชียและแปซิฟิก ครั้งที่ 4 (The 4th UNESCAP Ministerial Conference)
2545 รางวัลการพัฒนาที่ยั่งยืนจากการประชุมโจฮันเนสเบิร์ก
2554 OECD คัดเลือกให้เป็นเมืองแห่งการเติบโตสีเขียวแห่งแรกในเอเชีย
2556 OECD เผยแพร่รายงานการเติบโตสีเขียวของคิตะคิวชู
2559 การจัดการประชุมรัฐมนตรีด้านพลังงานของกลุ่ม G7
ศูนย์สังคมคาร์บอนต่ำในภูมิภาคเอเชีย (Kitakyushu Asian Center for Low Carbon Society)
โครงสร้าง
- เมืองคิตะคิวชู ð บริหารและประสานงาน
- สมาคมความร่วมมือด้านเทคโนโลยีเมืองคิตะคิวชู (KITA) ð ฝึกอบรมบุคลากรหรือจัดหาผู้เชี่ยวชาญ
- IGES Kitakyushu Urban Centre ð จัดทำโครงการวิจัย
ความร่วมมือ
- รัฐบาลกลางและหน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้อง
- JICA สาขาเมืองคิตะคิวชู
- บริษัทเอกชนหลายแห่งในพื้นที่
- สมาคมด้านอุตสาหกรรมและเศรษฐกิจต่าง ๆ
- สถาบันทางการศึกษาต่าง ๆ
- เมืองจากต่างชาติ
ความร่วมมือระหว่างเมืองกับประเทศในแถบเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
- การสถาปนาความสัมพันธ์เมืองพี่เมืองน้องสีเขียวกับเมืองสุราบายา สาธารณรัฐอินโดนีเซีย เมื่อ พ.ศ. 2555
ความร่วมมือ ด้านการกำจัดมูลฝอย
- การสถาปนาความสัมพันธ์เมืองพี่เมืองน้องกับเมืองไฮฟอง สาธารณรัฐสังคมนิยมเวียดนาม เมื่อ พ.ศ. 2557
ความร่วมมือ กำหนดแผนส่งเสริมการเติบโตสีเขียว (Green Growth Promotion Plan)
- การสถาปนาความสัมพันธ์เมืองพี่เมืองน้องกับกรุงพนมเปญ ราชอาณาจักรกัมพูชา เมื่อ พ.ศ. 2559
ความร่วมมือ คำแนะนำด้านการประปา (โครงการมหัศจรรย์กรุงพนมเปญ (Phnom Penh’s Miracle))
- การสถาปนาความสัมพันธ์เมืองพี่เมืองน้องสีเขียวกับเมืองดาเวา สาธารณรัฐฟิลิปปินส์ เมื่อ พ.ศ. 2560
ความร่วมมือ การผลิตพลังงานจากขยะ
ผู้นำเทคโนโลยีด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมของโลก
ได้ร่วมมือในโครงการต่าง ๆ กับ 80 เมือง จาก 16 ประเทศทั่วโลก จำนวนรวมมากกว่า 200 โครงการ อาทิ
- สาธารณรัฐประชาชนจีน ได้แก่ การควบคุมมลพิษทางอากาศ ค่าฝุ่นละอองขนาดเล็กกว่า 2.5 ไมครอน (PM2.5) ฯลฯ
- สาธารณรัฐอินเดีย ได้แก่ โครงการสาธิตโครงข่ายไฟฟ้าอัจฉริยะ (Smart Grid Demonstration Project) ฯลฯ
- สหพันธรัฐมาเลเซีย ได้แก่ สถานที่กำจัดมูลฝอยระยะยาว และการผลิตซีเมนต์ทางเลือกจากมูลฝอย ฯลฯ
- สาธารณรัฐแห่งสหภาพเมียนมา ได้แก่ การสร้างก๊าซชีวภาพ การจัดการมูลฝอย ฯลฯ
- ประเทศไทย ได้แก่ การส่งเสริมแนวคิดเมืองอุตสาหกรรมเชิงนิเวศที่สอดคล้องกับแต่ละชุมชน
โครงการจัดการมูลฝอย ณ เมืองสุราบายา สาธารณรัฐอินโดนีเซีย (ตั้งแต่ พ.ศ. 2545)
การดำเนินงาน การแยกประเภทขยะ การทำปุ๋ย การรีไซเคิล
ผลการดำเนินงาน มีจำนวนมูลฝอยลดลง 30% (พ.ศ. 2548-2553) มีการประดับถนนด้วยดอกไม้และมีการพัฒนาความตระหนักด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมของประชาชน
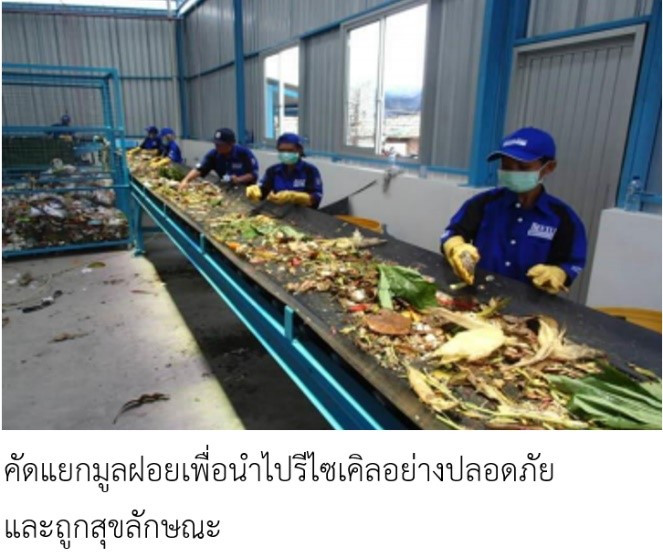
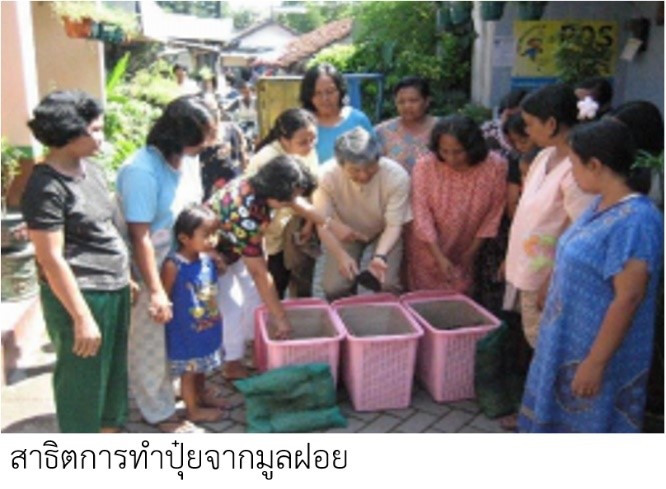


โครงการจัดการมูลฝอย ณ กรุงพนมเปญ ราชอาณาจักรกัมพูชา
มาตรการเพื่อรับมือกับปริมาณขยะที่เพิ่มขึ้นอย่างรวดเร็วเนื่องจากจำนวนประชากรมากขึ้นและการเติบโตทางเศรษฐกิจ
ระยะเวลา พ.ศ. 2561-2563 (3 ปี)
เงินทุน JICA ให้เงินสนับสนุน 550,000 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ (หรือประมาณ 17,600,000 บาท)
หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้อง เมืองคิตะคิวชู KITA บริษัทเอกชนในเมืองคิตะคิวชู กรุงพนมเปญ CINTRI องค์การ
ไม่แสวงหาผลกำไรในกรุงพนมเปญ ฯลฯ
 |
|
พิธีลงนามข้อตกลงการสถาปนาความสัมพันธ์เมืองพี่เมืองน้องฯ
|
การทำงานร่วมกับโครงการสิ่งแวดล้อมแห่งสหประชาชาติ (UNEP)
เมืองคิตะคิวชูและโครงการสิ่งแวดล้อมแห่งสหประชาชาติได้ร่วมกันจัดงานแถลงข่าวเมื่อวันที่ 2 สิงหาคม 2562 เพื่อประกาศความตกลงในการส่งเสริมความสัมพันธ์เพื่อลดขยะในทะเล
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญจากเมืองคิตะคิวชูจะให้การสนับสนุนรัฐบาลท้องถิ่นในประเทศไทยและประเทศกัมพูชาเพื่อช่วยดำเนินการตามแผนการจัดการมูลฝอยอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพต่อไปในอนาคต

“แผนงานด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมขั้นพื้นฐานของเมืองคิตะคิวชู (The Kitakyushu City Basic Environment Plan)” หัวข้อย่อย “แผนงานเพื่อการตระหนักถึงทุนธรรมชาติและเป้าหมายการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน (Environmental Capital & SDGs Realization Plan)”
คือแผนงานเพื่อความตระหนักถึงโครงการสุดยอดการออกแบบเมืองหลวงแห่งการพัฒนาที่ยั่งยืนของโลก (The Grand Design for a World Capital of Sustainable Development)
เป้าหมายของนโยบาย
- การพัฒนาด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมซึ่งมุ่งเน้นการดำเนินกิจกรรมในระดับรากหญ้าและการสร้างตราสินค้าด้าน
สิ่งแวดล้อมของเมืองคิตะคิวชู
- ความตระหนักถึงสังคมคาร์บอนต่ำภายในปี 2593 และสังคมหลังคาร์บอน
- การสร้างระบบหมุนเวียนชั้นนำของโลก
- การพัฒนาเมืองที่มีคุณภาพ และการบูรณาการสิ่งแวดล้อม เศรษฐกิจ และสังคม
ระยะเวลา ปีงบประมาณ 2560-2564
เขตพื้นที่ เมืองคิตะคิวชู และที่อื่น ๆ ในต่างประเทศ
แผนการดำเนินงานเพื่อให้สอดคล้องกับเป้าหมายการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน
|
SDGs
|
แผนงานด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมขั้นพื้นฐาน
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมธนาคารอาหารที่มีประสิทธิภาพ ลดการเหลือทิ้งอาหาร และสร้าง ความตระหนักถึงปฏิญญาเพื่อการไม่มีอาหารเหลือทิ้ง (No Leftovers Declaration) (2.1 และ 2.2)
· การส่งเสริมมาตรการเพื่อรับมือกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศ (2.4)
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมเมืองขนาดกะทัดรัด และการขนส่งสาธารณะ (3.6)
· กระบวนการจัดการสารเคมีที่มีอันตรายอย่างเหมาะสม (3.9)
· การรักษาสิ่งแวดล้อมทางอากาศ น้ำ และดิน (3.9)
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมโดยใช้วิธีการศึกษาเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสิ่งแวดล้อม การศึกษาเพื่อการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน (ESD) การทดสอบ World Environment Capital Examination การทำกิจกรรม Eco Life Stage ฯลฯ (4.7)
· การฝึกอบรมให้กับผู้สนใจจากแถบเอเชียและภูมิภาคอื่น ๆ การศึกษาขั้นสูงด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมในต่างประเทศ และการส่งเสริมกิจกรรมความร่วมมือด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมระหว่างประเทศ (4.7)
|
  |
· กระบวนการจัดการสารเคมีที่มีอันตรายอย่างเหมาะสม (6.3)
· การรักษาระบบนิเวศและชนิดพันธุ์ และการดำเนินโครงการป่า-หมู่บ้าน-แม่น้ำ-ทะเล (6.6)
· การรักษาสิ่งแวดล้อมทางอากาศ น้ำ และดิน (6.3)
|
 |
· การเริ่มใช้พลังงานทดแทนขนาดใหญ่ เช่น พลังงานแสงอาทิตย์ ลม และสร้างศูนย์อุตสาหกรรมเพื่อพัฒนาเทคโนโลยีไฮโดรเจนและอุตสาหกรรมการผลิตไฟฟ้าจากพลังงานลม (7.2)
· การส่งเสริมการประหยัดและการจัดการพลังงาน (7.3)
· การส่งเสริมพลังงานทดแทนและการประหยัดพลังงานในภูมิภาคเอเชียผ่านศูนย์คาร์บอนต่ำแห่งเอเชีย (The Asian Low-Carbon Center) (7.2 และ 7.3)
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมการพัฒนาให้เมืองคิตะคิวชูเป็นแหล่งพลังงานในท้องถิ่นรวมถึงพลังงานทดแทน และการจัดการพลังงาน ฯลฯ (8.1 and 8.2)
· การพัฒนาเมืองนิเวศ (Eco Town) และอุตสาหกรรมการรีไซเคิล (8.1, 8.2 และ 8.4)
· การใช้ประโยชน์จากแหล่งท่องเที่ยวทางธรรมชาติ (8.9)
· การส่งเสริมอุตสาหกรรมและธุรกิจระหว่างประเทศด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม (8.1 และ 8.2)
|
 |
· การก่อสร้างที่พักอาศัยที่มีคุณภาพ และการจัดทำวัสดุคงคลัง (9.1)
· การส่งเสริมอุตสาหกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคาร์บอนต่ำและพลังงาน (9.4 และ 9.5)
· การพัฒนาเมืองนิเวศ (Eco Town) และอุตสาหกรรมการรีไซเคิล (9.4 และ 9.5)
· การส่งเสริมมาตรการเพื่อรับมือกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศ และการลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติทางระบบนิเวศ (9.1)
· การพัฒนาเทคโนโลยีด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมโดยทำงานร่วมกับสถาบันทางการศึกษาต่าง ๆ
ฯลฯ (9.5)
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมเมืองขนาดกะทัดรัด และการขนส่งสาธารณะ (11.2)
· การส่งเสริมโครงการปลูกป่าในเมือง (11.7)
· กระบวนการจัดการสารเคมีที่มีอันตรายอย่างเหมาะสม (11.6)
· การรักษาสิ่งแวดล้อมทางอากาศ น้ำ และดิน (11.6)
· การส่งเสริมมาตรการเพื่อรับมือกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศ และการลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติทางระบบนิเวศ (11.5)
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมการเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับสิ่งแวดล้อม การศึกษาเพื่อการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน (ESD) ฯลฯ (12.8)
· การส่งเสริมความคิดริเริ่ม “การลดขยะ การนำกลับมาใช้ใหม่ และการรีไซเคิล (3Rs+)” และกิจกรรมการรีไซเคิลที่ทันสมัย และเพิ่มอัตราส่วนการรีไซเคิลทรัพยากร (12.2, 12.4 และ 12.5)
· การส่งเสริมธนาคารอาหารที่มีประสิทธิภาพ ลดการเหลือทิ้งอาหาร และสร้างความตระหนักถึงปฏิญญาเพื่อการไม่มีอาหารเหลือทิ้ง (No Leftovers Declaration) (12.3)
· การส่งเสริมรางวัลคิตะคิวชูอีโคพรีเมี่ยม (The Kitakyushu Eco Premium Awards) ฯลฯ (12.4, 12.6 และ 12.7)
|
 |
· การส่งเสริมการเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับสิ่งแวดล้อม การศึกษาเพื่อการพัฒนาอย่างยั่งยืน (ESD) ฯลฯ (13.3)
· การส่งเสริมความพยายามในการตระหนักถึงสังคมคาร์บอนต่ำพิเศษ (13.1 และ 13.3)
· การส่งเสริมการใช้ทรัพยากรอย่างคุ้มค่า และการผลิตพลังงานจากขยะ (13.1)
การส่งเสริมมาตรการเพื่อรับมือกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศ และการลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติทางระบบนิเวศ (13.1)
|
 |
· การปฏิบัติตามกระบวนการในการควบคุมขยะทะเล และกระบวนการจัดการสารเคมีที่มีอันตรายอย่างเหมาะสม (14.1)
· การรักษาระบบนิเวศและชนิดพันธุ์ และการดำเนินโครงการป่า-หมู่บ้าน-แม่น้ำ-
ทะเล (14.2)
· การรักษาสิ่งแวดล้อมทางอากาศ น้ำ และดิน (14.1)
|
 |
· การดูแลรักษาและการใช้ประโยชน์จากทุนธรรมชาติผ่านการจัดการป่าไม้
ที่เหมาะสม ฯลฯ (15.1, 15.2, 15.4 และ 15.5)
· การรักษาระบบนิเวศและชนิดพันธุ์ และการดำเนินโครงการป่า-หมู่บ้าน-แม่น้ำ-ทะเล (15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4 และ 15.5)
· การแก้ปัญหามดคันไฟและชนิดพันธุ์ต่างถิ่น (15.8)
· การประเมินมูลค่าของทุนธรรมชาติ (15.9)
การประเมินผลที่เหมาะสม (15.1, 15.2, 15.4 และ 15.5)
|
 |
การส่งเสริมความร่วมมือและกิจการระหว่างประเทศด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม ความตระหนัก
ถึงสังคมคาร์บอนต่ำในภูมิภาคเอเชีย การจัดตั้งศูนย์รีไซเคิลทรัพยากรระหว่างประเทศและการพัฒนาอุตสาหกรรมระหว่างประเทศด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม (17.7, 17.9, 17.16 และ 17.17)
|
แหล่งที่มาของข้อมูล
กองยุทธศาสตร์ด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมระหว่างประเทศ สำนักสิ่งแวดล้อม เมืองคิตะคิวชู. 2561. Kitakyushu, as Green Growth City. ค้นเมื่อ 15 พฤษภาคม 2563. แหล่งที่มา:https://www.uncrd.or.jp/content/documents/6345MS-1-P3.pdf.
กองการป้องกันภาวะโลกร้อน สำนักสิ่งแวดล้อม เมืองคิตะคิวชู. (-). City of Kitakyushu. ค้นเมื่อ 15 พฤษภาคม 2563. แหล่งที่มา:https://www.uncrd.or.jp/content/documents/5634Presentation%204%20-%20Module%206%20-%20Mr.%20Mitoma-Kitakyushu.pdf.
สำนักสิ่งแวดล้อม เมืองคิตะคิวชู. The Kitakyushu City Basic Environment Plan Subtitle: Environmental Capital & SDGs Realization Plan. ค้นเมื่อ 15 พฤษภาคม 2563. แหล่งที่มา: https://ssl.city.kitakyushu.lg.jp/files/000822648.pdf.
องค์การสหประชาชาติ. 2563. Sustainable Development Goals. ค้นเมื่อ 15 พฤษภาคม 2563. แหล่งที่มา: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdgs.
2556. Green Growth in Kitakyushu, Japan. ค้นเมื่อ 15 พฤษภาคม 2563. แหล่งที่มา: https://read.oecd-ilibrary.org/urban-rural-and-regional-development/green-growth-in-kitakyushu-japan_9789264195134-en#page1.
Junko, O., Kaori, H., Shiko, H., Junichi F., Yatsuka, K. 2561. Kitakyushu City the Sustainable Development Goals Report. ค้นเมื่อ 15 พฤษภาคม 2563. แหล่งที่มา:
https://www.iges.or.jp/en/publication_documents/pub/policyreport/en/6569/Kitakyushu_SDGreport_EN_201810.pdf
Kitakyushu Green Growth City
Introduction
Kitakyushu City is located in Fukuoka Prefecture on the western end of Kyushu archipelago. Since 1901, the city has developed as a manufacturing city, which resulted in major air and water pollution around 1960s. Many stakeholders, especially citizens, worked hard to improve the situation and nowadays blue sky and ocean can be seen in Kitakyushu. These experiences enabled Kitakyushu City to develop new industries including environmental technology. It has been developing into a smart, eco-city with resource circulation and renewable energy resources.
Agenda
1. Industrial Development & Overcoming Pollution
2. International Environmental Cooperation & Business
3. Role of Kitakyushu to promote SDGs
Kitakyushu leads as environmental advanced city
1996 Agenda 21
1998 Kitakyushu Eco-Town Project
2000, 2006 User fees system for waste disposal
2004 Environmental Capital of the World Grand Design
2009 ECO-Model City (designated by national government)
2012 Future City Initiative & Int’l Strategic Zone Model City (designated by national government)
2017 Basic Environmental Plan incorporating SDGs
Environmental Technologies

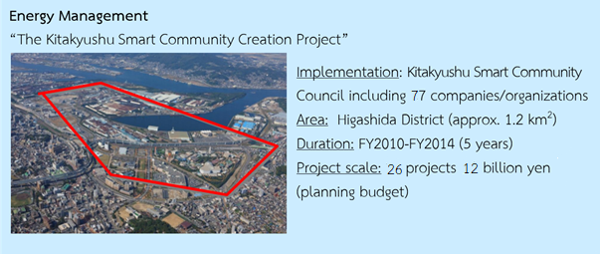

International Evaluation of Kitakyushu
1985 White paper by OECD for the city transformation “From Gray City to Green City” 1990 Global 500 Award from UNEP
1992 Local Government Honours at the Rio Summit
2000 The 4th UNESCAP Ministerial Conference in Kitakyushu
2002 Sustainable Development Award at the Johannesburg Summit
2011 The first Asian Green Growth City selected by OECD
2013 OECD issued the Report on Kitakyushu’s Green Growth.
2016 G7 Kitakyushu Energy Ministerial Meeting
Kitakyushu Asian Center for Low Carbon Society
The engine of Kitakyushu for building low carbon societies in Asia through environmental business skills, since 2010.
Structure
- City of Kitakyushu ð Administration and coordination
- Kitakyushu International Technocooperative Association ð Training of personnel or dispatch of experts
- IGES Kitakyushu Urban Centre ð Research projects
Collaboration
- National government, and relevant organizations
- JICA Kyushu Center
- Local private companies
- Industrial and economic associations
- Academic institutions
- Oversea cities
City-to-City Cooperation with South East Asian Countries
- Surabaya, Indonesia “Green Sister City” since 2012
Cooperation: Composting of food waste
- Hai Phong, Viet Nam “Sister City” since 2014
Cooperation: Green Growth Promotion Plan was formulated.
- Phnom Penh, Cambodia “Sister City” since 2016
Cooperation: Waterworks Guidance (Phnom Penh’s Miracle)
- Davao in Philippines “Green Sister City” since 2017
Cooperation: Introducing Waste to Energy Facilities
Environmental technologies of Kitakyushu, leading the world
* About 80 cities in 16 counties * Over 200 projects such as
- China: Air pollution control of PM2.5 etc.
- India: Smart Grid Demonstration Project etc.
- Malaysia: life-longer of waste disposal site, Producing alternatives for cement from waste etc.
- Myanmar: Biogas Generation, Waste Management etc.
- Thailand: Promotion of Eco-Industrial Town Concept based on communities
Waste Management Projects in Surabaya, Indonesia (since 2002)
Implementation: Separation, composting and recycling
Outcome: 30% reduction of solid waste from 2005 to 2010, streets decorated with flowers and improvement of public environmental awareness

Waste Management Project in Phnom Penh, Cambodia
Measuring to cope with rapid increase in waste generation volume due to population increase and high economic growth
Duration: 2018-2020 (3 years)
Fund: US$ 550,000 by JICA
Entities: City of Kitakyushu, KITA, private companies in Kitakyushu, Phnom Penh Capital City, CINTRI, Local NGO in Phnom Penh, etc.

Linkages with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
On August 2, 2019, Kitakyushu and UNEP held a joint press conference to announce their agreement on strengthening cooperation to reduce marine litter.
In the future, experts from Kitakyushu will provide support to local governments in Thailand and Cambodia to help implement effective waste management plans.

“The Kitakyushu City Basic Environment Plan” Subtitled “Environmental Capital & SDGs Realization Plan”
What is it?
It is realization of the Grand Design on World Capital of Sustainable Development in 2014
In 2015 the countries of the world gathered together to make the Paris Agreement. Based on
this agreement, it is necessary to proceed with concrete measures to tackle global warming. and attain SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals).
Policy Targets:
1. Environmental development which is oriented by grassroots activism and establishment ofKitakyushu Environmental Brand
2. Realization of an ultra-low carbon society by 2050 and a post-carbon society
3. Creation of a world-leading circular system
4. Quality urban development and integrated improvement of environment, economy and society
Duration: FY 2017 to FY 2021
Area: mainly in Kitakyushu City and broad-ranging perspectives including overseas
Contribution to SDGs
|
SDGs
|
The Basic Environment Plan
|
 |
· Promotion of effective use of food-banks, reducing food loss and raising awareness of the No Leftovers Declaration (2.1 and 2.2)
· Strengthening measures to deal with climate change (2.4)
|
 |
· Promotion of a compact city and public transportation (3.6)
· Appropriate processing and management of chemical and hazardous substances (3.9)
· Protection of air, water and soil environments (3.9)
|
 |
· Fostering environmental experts through environmental learning, ESD, World Environment Capital Examination, Eco Life Stage, etc. (4.7)
· Accept trainees from Asia and other regions, advance overseas environmental education and promote international environmental cooperation activities. (4.7)
|
 |
· Appropriate processing and management of chemical and hazardous substances (6.3)
· Preserving ecosystems and species and the Forest-Village-River-Sea (6.6)
· Protection of air, water and soil environments (6.3)
|
 |
· Introduction of large-scale renewable energy such as solar and wind, and building an industrial center for developing hydrogen technology and wind power generation industries (7.2)
· Promotion of energy saving and management (7.3)
· Promotion of renewable energy and energy saving in the Asian region through the Asian Low-Carbon Center (7.2 and 7.3)
|
 |
· Promotion of development as a local energy base including renewable energy and energy management, etc. (8.1 and 8.2)
· Advancement of Eco Industrial Town and recycling industries
(8.1, 8.2 and 8.4)
· Utilize natural tourism resources (8.9)
· Promotion of the fostering of environmental industries and international business (8.1 and 8.2)
|
 |
· Building quality housing and material stock (9.1)
· Promotion of low-carbon and energy related industries (9.4 and 9.5)
· Advancement of Eco Town and recycling industries (9.4 and 9.5)
· Strengthening measures to deal with climate change and ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction (9.1)
· Development of environmental technology through collaboration with academic institutions, etc. (9.5)
|
 |
· Promotion of a compact city and public transportation (11.2)
· Promotion of urban afforestation projects (11.7)
· Appropriate processing and management of chemical and hazardous substances (11.6)
· Protection of air, water and soil environments (11.6)
· Strengthening measures to deal with climate change and ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction (11.5)
|
 |
· Promotion of environmental learning, ESD, etc. (12.8)
· Promotion of the ‘3Rs Plus’ initiative and advanced recycling activities and improving resource recycling ratio (12.2, 12.4 and 12.5)
· Promotion of effective use of food-banks, reducing food loss and raising awareness of the No Leftovers Declaration (12.3)
· Promotion of the Kitakyushu Eco Premium Awards, etc. (12.4, 12.6 and 12.7)
|
 |
· Promotion of environmental learning, Education for Sustainable Development (ESD), etc. (13.3)
· Promotion of efforts to realize an ultra-low carbon society (13.1 and 13.3)
· Promotion of efficient use of resources, waste power generation (13.1)
· Strengthening measures to deal with climate change and ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction (13.1)
|
 |
· Taking steps to control marine litter and appropriate processing and management of chemical and hazardous substances (14.1)
· Preserving ecosystems and species, and the Forest-Village-River-Sea (14.2)
· Protection of air, water and soil environments (14-1)
|
 |
· Maintenance and good use of natural capital through the proper forest management, etc. (15.1, 15.2, 15.4 and 15.5)
· Preserving ecosystems and species, and the Forest-Village-River-Sea (15.1, 15.2, 15.3, 15.4 and 15.5)
· Tackling fire ants and other alien species (15.8)
· Assessment of the value of natural capital (15.9)
· Appropriate assessments (15.1, 15.2, 15.4 and 15.5)
|
Sources:
International Environmental Strategies Division of Environment Bureau of Kitakyushu City. (2018) Kitakyushu, as Green Growth City. Retrieved 15 May 2020. from https://www.uncrd.or.jp/content/documents/6345MS-1-P3.pdf.
Global Warming Prevention Division of Environment Bureau of Kitakyushu City. (-) City of Kitakyushu. Retrieved 15 May 2020. From https://www.uncrd.or.jp/content/documents/5634Presentation%204%20-%20Module%206%20-%20Mr.%20Mitoma-Kitakyushu.pdf.
Environment Bureau of Kitakyushu City. (2017). The Kitakyushu City Basic Environment Plan Subtitle: Environmental Capital & SDGs Realization Plan. Retrieved 15 May 2020. From https://ssl.city.kitakyushu.lg.jp/files/000822648.pdf
(2019) Sustainable Development Goals. Retrieved 15 May 2020. From https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdgs.
(2013). Green Growth in Kitakyushu, Japan. Retrieved 15 May 2020. From
https://read.oecd-ilibrary.org/urban-rural-and-regional-development/green-growth-in-kitakyushu-japan_9789264195134-en#page1.
Junko, O., Kaori, H., Shiko, H., Junichi F., Yatsuka, K. (2018). Kitakyushu City the Sustainable Development Goals Report. Retrieved 15 May 2020. From
https://www.iges.or.jp/en/publication_documents/pub/policyreport/en/6569/Kitakyushu_SDGreport_EN_201810.pdf.
เอกสารแนบ : Best Practice - จังหวัดฟูกูโอกะ Green Growth (พรรณระวี).pdf